Energy efficiency
Energy efficiency: reducing consumption, a major issue! Reducing energy consumption is a crucial goal for companies. Measurement is the only way to achieve it.
 At the heart of companies' and all other organizations' strategies, the improvement of energy efficiency helps to reduce costs and shrink their carbon footprint.
At the heart of companies' and all other organizations' strategies, the improvement of energy efficiency helps to reduce costs and shrink their carbon footprint.
This is a crucial goal in the current economic and environmental context.
Find out more
To help organizations to structure their approach to achieving this objective, standards have been developed to define an energy management system. The ISO 50001 standard recommends, for example, a methodology based on "Plan-Do-Check-Act".
In particular, it defines energy planning and measurement verification phases to draw up a precise diagnosis of the initial situation (identification of energy-hungry areas) and check the effectiveness of the action taken to improve energy efficiency.
Whether the approach is covered by the ISO 50001 system or not, energy efficiency improvement necessarily includes a diagnostic phase involving precise analysis of energy consumption (analysis of the consumption profile and detailed breakdown of consumption).
This helps to identify potential ways of reducing consumption in the major areas, which may lead to modification of the industrial processes, modernization of equipment and machines, building improvement works or changes in personal habits.
Once this action has been taken, checks are performed to ensure that the improvements match the forecasts and, if necessary, to implement corrective action.
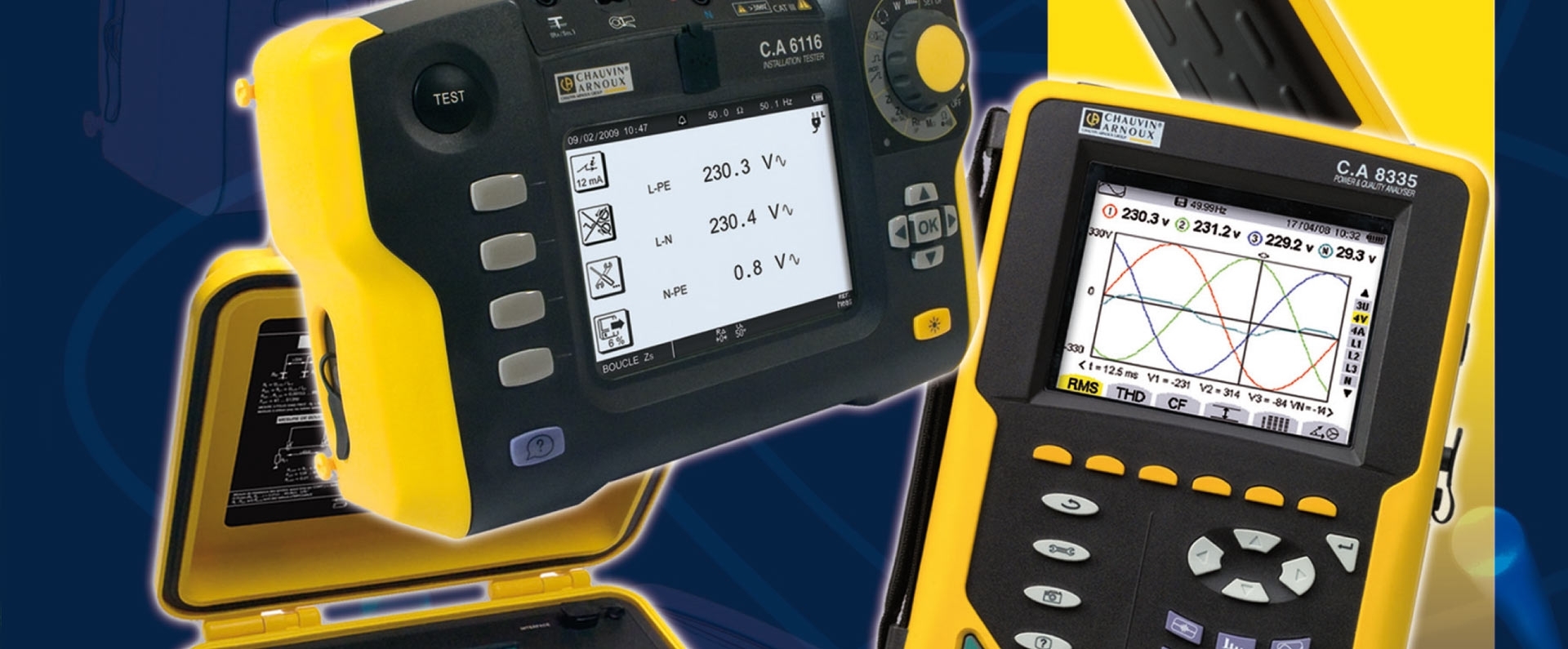
Finding out what you consume… Analysis
 Finding out what you consume is a central part of any energy efficiency initiative.
Finding out what you consume is a central part of any energy efficiency initiative.
By placing power and energy loggers or power analysers on the different electrical feeders downstream from the meter, you can assess the relative weight of each line as part of global consumption, simply and without interrupting the installation's operation, and define a load profile for the installation so that you can determine the priorities regarding orientations for improvements.
Find out more
To complete these initial surveys, a comprehensive range of loggers is available to measure and automatically record the trends over time of voltages, currents, temperatures and process signals.
Analysis of these additional measurements provides essential information for thoroughly understanding the consumption profiles and checking the effectiveness of the modifications made to improve overall energy efficiency.
Point measurements of physical quantities such as temperature, air flow, pressure and lighting can also help you to determine potential ways of improving energy efficiency.
Lastly, thermal cameras are essential tools for drawing up an energy survey of a building. Practical and simple to use, they can detect faults and anomalies such as:
- Thermal bridges
- Poor positioning or absence of insulants
- Infiltration,
- Materials damaged by humidity
- Joints around openings which are no longer leakproof
These are all factors which cause excess consumption.
Analysis of the measurements… Diagnosis
 Once all the measurements have been performed and noted, a diagnosis (Enerdis link) is drawn up for the implementation of corrective action.
Once all the measurements have been performed and noted, a diagnosis (Enerdis link) is drawn up for the implementation of corrective action.
A comparison is made between the theoretical efficiency of an installation and the actual measurements.
Several types of corrective action may be taken: resizing of the transformer, implementation of filtering systems, replacement of faulty equipment, etc;
This analysis enables you to provide the best solution in the right place at the right time.
A few examples
A few examples:
- Measurement of the K factor for resizing of the power transformer
http://www.chauvin-arnoux.com/fiches/pdf/fr/Appli_facteur_K.pdf
- Sizing of the capacitor banks for power factor correction
- Reduce you electricity bill!
http://www.chauvin-arnoux.com/fiches/pdf/fr/fiche_appli_mesure_compensation.pdf
For thermal diagnostics on buildings, comparison between the theoretical energy yield and the energy input which it requires helps to determine the improvement work needed.
Depending on the heating, air-condition and ventilation equipment to be set up permanently (e.g. for data centres), the use of thermography before positioning the equipment can help to define an arrangement optimizing both comfort and energy consumption.
Thermal analysis clearly shows hot and cold areas and the thermal exchanges between equipment items.
Checking effectiveness: Testing
 Once the solutions have been implemented, you need to repeat the measurements performed during the audit before correction. Monitoring can then be set up to check that the day-to-day savings achieved persist over time and to avoid the reappearance of drift.
Once the solutions have been implemented, you need to repeat the measurements performed during the audit before correction. Monitoring can then be set up to check that the day-to-day savings achieved persist over time and to avoid the reappearance of drift.
At this stage, it may be decided to define new improvement targets or to take corrective action to achieve or improve on the initial objective.
Measurement is therefore an essential technique on the energy efficiency improvement process.
Measurement of savings
http://pel100.com/fr/le-produit/fonctionnalites/comptage.aspx
Clean energy sources
 In the context of sustainable development, the share of clean energy has grown significantly in recent years.
In the context of sustainable development, the share of clean energy has grown significantly in recent years.
This includes solar energy. The photovoltaic sector (transforming solar energy into electrical energy), rolled out both in homes and on high-capacity production sites (solar farms) is a major focus for us.
To assess the efficiency of these installations and check solar panels, Chauvin Arnoux proposes solar panel testers specially designed for this application.